WebSplitter:
A Unified XML Framework For
Multi-Device Collaborative Web Browsing
WebSplitter symbolizes the union of
pervasive
multi-device computing and collaborative multi-user computing.
WebSplitter
provides a unified XML framework that enables both multi-device and
multi-user
Web browsing, as shown below.
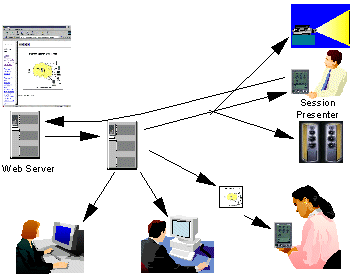
WebSplitter splits a requested XML
Web page
and delivers the appropriate partial view of each page to each user, or
more accurately to each user’s set of devices. Multiple users can
participate in the same browsing session, as in traditional
conferencing
groupware. Depending on the access privileges of the user to the
different components of content on each page, WebSplitter generates a
personalized
partial view. WebSplitter further splits the partial view among
the
devices available to each user, e.g. laptop, wireless PDA,
projection
display, stereo speakers.
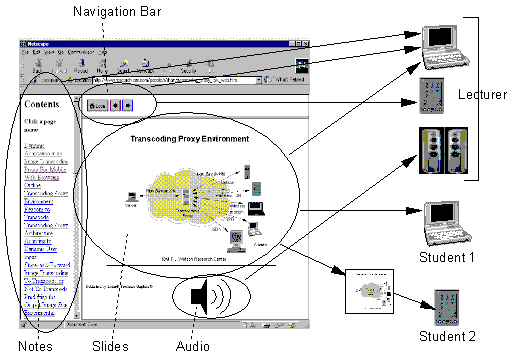
An author could compose a
presentation whose
different components are delivered to different users and end devices
depending
on a set of tag mapping rules specified by the page author. The
author
may define different groups of users with different access privileges,
e.g. to provide different levels of learning, to hide information from
certain groups, or to provide different levels of parental
control.
Any browsing device could access such an authored page.
For example, a lecturer could use a
wireless
PDA to browse such a "WebSplit" page, and spread the resulting
presentation
around nearby or even remote devices. In effect, the wireless PDA
would act a remote control for the multimedia capabilities of nearby
devices.
The lecturer would use the PDA to orchestrate a composite presentation
across a set of devices available in the lecture hall. Moreover,
other remote distance learners could follow the lecturer's browsing
session.
We envision many more applications
that could
benefit from this WebSplitting capability.
The architecture consists of
-
an XML metadata policy file defining
access privileges
to XML tags on a Web page
-
a middleware proxy that splits XML
Web content
to create partial views
-
a client-side component, e.g.
applet, enabling
user login and reception of pushed browsing data
Service discovery finds and registers
proxies,
browsing sessions, and device capabilities.
We have demonstrated the feasibility
of splitting
the different tags in an XML Web page to different end users’ browsers,
and of pushing updates from the browsing session to heterogeneous
devices,
including a laptop and a PDA.
WebSplitter was published in ACM CSCW
2000.
The precise reference is
-
R. Han, V. Perret, M. Nagshineh,
"WebSplitter:
A Unified XML Framework for Multi-Device Collaborative Web
Browsing,"
ACM Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work (CSCW) 2000, pp.
-. [pdf
(296 KB)]

Last updated:
October 11,
2000
|