




















| Primary Actor | Goal in Context |
| Scope | Level |
| Stakeholders and Interests | Precondition |
| Minimal Guarantees | Success Guarantees |
| Trigger | Main Success Scenario |
| Extensions | Technology and Data Variations List |
| Priority | Releases |
| Response Time | Frequency of Use |
| Channel to Primary Actor | Secondary Actors |
| Channels to Secondary Actor | Open Issues |
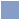
Use Case Narratives
Use case narratives are used to motivate the existence of a use case. They are not use cases themselves!

User-Level Use Case

Summary-Level Use Case

Low-Ceremony Use Case

High-Ceremony Use Case



| Function Type | Simple | Average | Complex |
|---|---|---|---|
| External Input | 3 | 4 | 6 |
| External Output | 4 | 5 | 7 |
| Logical Internal File | 7 | 10 | 15 |
| External Interface File | 5 | 7 | 10 |
| External Inquiry | 3 | 4 | 6 |
for i in each parameter
for j in each classification
UFP = UFP + weight[i][j] * count[i][j]| Item | Equation | Score |
|---|---|---|
| 3 simple external inputs | 3 * 3 | 9 |
| 2 complex external inputs | 2 * 6 | 12 |
| 1 average external output | 1 * 5 | 5 |
| 2 average logical internal files | 2 * 10 | 20 |
| 2 complex external inquiries | 2 * 6 | 12 |
| Final UFP | 58 |
| Environmental Factors | |
|---|---|
| data communications | distributed processing |
| performance objectives | operation configuration load |
| transaction rate | on-line data entry |
| end user efficiency | on-line update |
| complex processing logic | re-usability |
| installation ease | operational ease |
| multiple sites | desire to facilitate change |