




















| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Error | a mistake made by a programmer. Implies that for some input i, F(i) ≠ expected output |
| Fault | an incorrect state of a program that is entered due to an error. Some errors don’t cause failures right away, every state between the error and the failure are faults For this class, however, you can think of a “fault” as being the location in the code where the error exists |
| Failure | a symptom of an error. For example, a crash, incorrect output, incorrect behavior, … |
if (x < y)
if (x <= y)
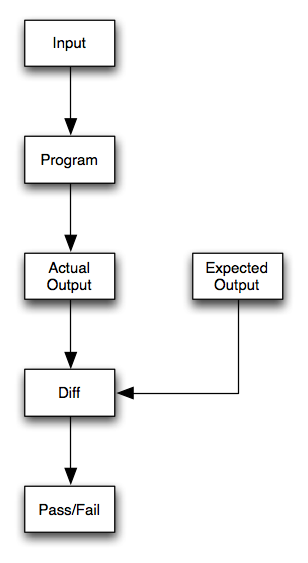
A test case consists of:
| Input | The specific values given to a program |
| Expected Output | The output predicated by a program's specification |
| Documentation | What type of failure is this test case testing? |
Test cases are applied to a program during a test run. A test run consists of:
| Actual Output | The output generated by a program when given the input of a test case |
| Pass/Fail Grade | Did the actual output match the expected output? |
Test runs are typically supported by a “testing harness” or “test scaffolding”. This refers to the software that helps you perform (or sometimes automate) test runs
|
 |
int GreatestCommonDivisor(int x, int y)
To test exhaustively is impossible (both parameters can take on an infinite number of values) but with 5 categories identified, we can get by with only 5 test cases!